Gurudwaras in Fiji
Unlike the majority of Fiji’s Indian population, who are descendants of Indian indentured labourers brought to Fiji between 1879 and 1916, most of the Sikhs came to Fiji as free immigrants. Most Sikhs established themselves as farmers. Sikhs also came to Fiji as policemen, teachers and preachers. In recent years large numbers of Sikhs have emigrated from Fiji, especially to the United States. Sikhs in Fiji are generally referred to as Punjabis.
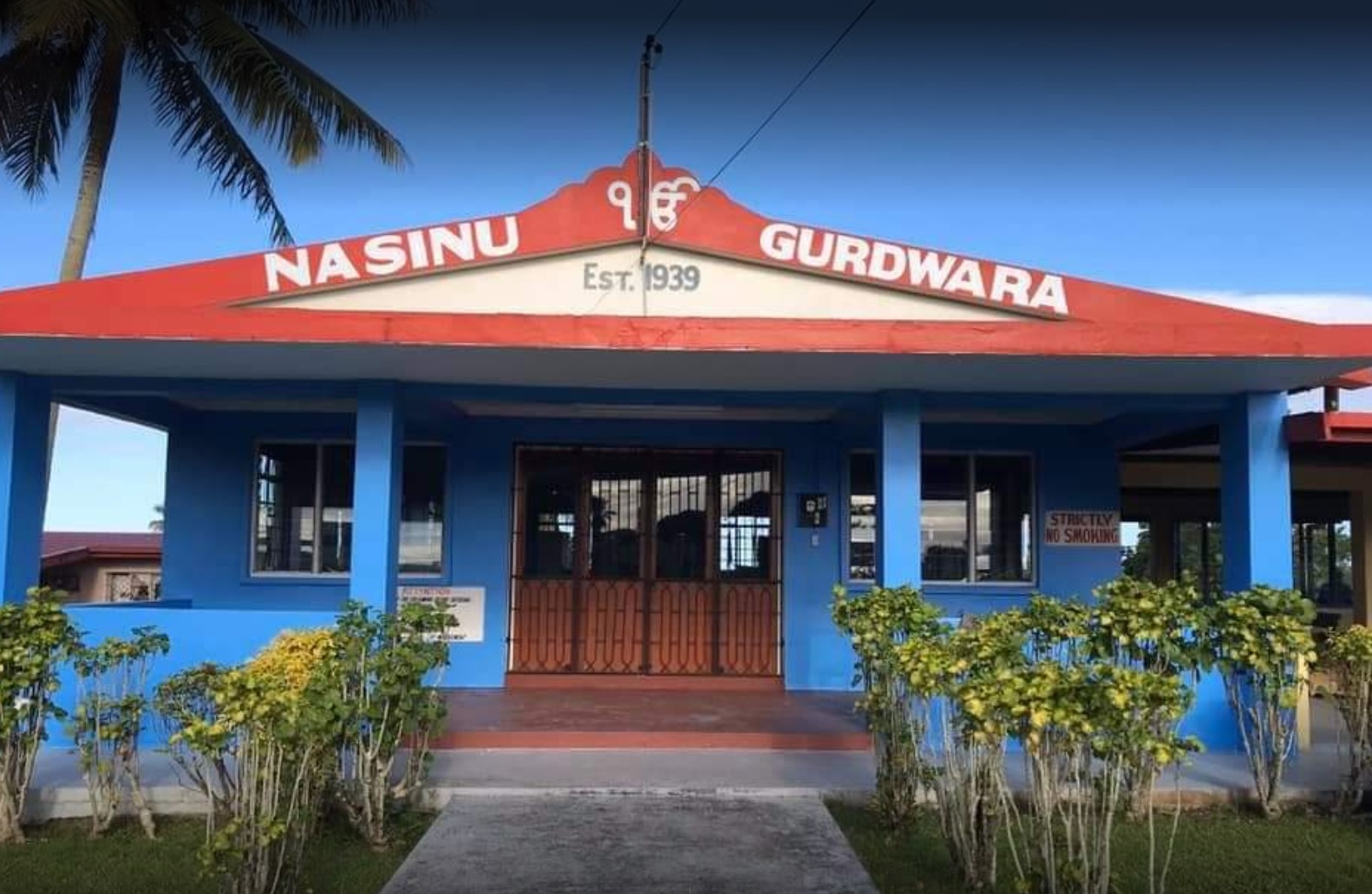
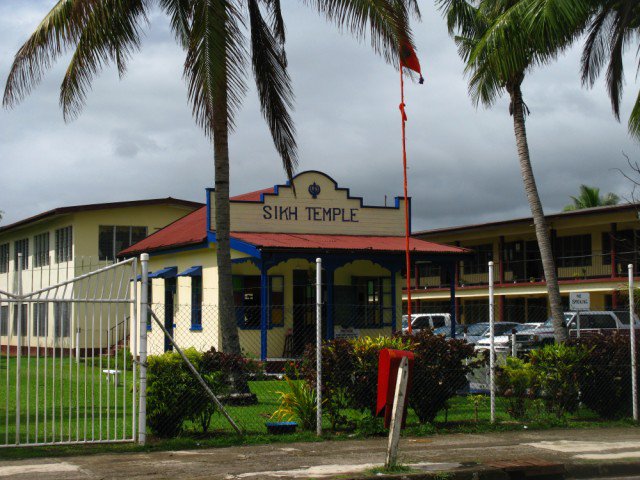
Sikh temples have in established in areas of Fiji where there is a concentration Sikhs. These temples do not only serve as places of worship but as a place where the food and shelter were provided for the needy. The first Sikh temple in Fiji was built in Samabula (near Suva) in 1922 to provide for the needs of new Sikh migrants. Once Tamavua and Nasinu areas (near Suva) had a large concentration of Sikhs and in 1944 a temple was established in Nasinu. Most Sikhs from the settlements around Suva have emigrated to the United States and Canada and some have moved to the Western Division to undertake cane farming. There is a concentration of Sikh cane farmers in Mataniqara and Tagitagi which lie between Ba and Tavua and to cater for their needs, a temple was built in Tagitagi. There is another temple in Lautoka City, built to cater for the needs of the Sikhs in the Sabeto Valley, but many of these have either left for overseas or moved into the naighbouring settlement of Vutualevu. There is only one temple outside the main island of Viti Levu and it is located in the town of Labasa in the second largest island of Vanua Levu. All the temples in Fiji, except the one in Nasinu, are controlled by temple committees and funded by donations from the local Sikh community
If there are any omissions or errors in Gurudwara Sahibs listed in Fiji or there are additional Gurudwaras in Fiji, Please Contact Us with details.

Sikh temples have in established in areas of Fiji where there is a concentration Sikhs. These temples do not only serve as places of worship but as a place where the food and shelter were provided for the needy. The first Sikh temple in Fiji was built in Samabula (near Suva) in 1922 to provide […]
Once Tamavua and Nasinu areas (near Suva) had a large concentration of Sikhs and in 1943 First Shree Guru RaviDas Gurudwara was established in Nasinu 6 miles.The founding fathers of this Guru RaviDas Gurudwara (a.k.a) AD-Punjab Association came from Punjab India in early 1900s. Registered trustee’s are Mr. Lachhu Ram a.k.a. Lachhu Sheemar (f/n) Khema […]
Lautoka Gurudwara Fiji The Gurudwara was founded in 1933 by the newly arrived sikh immigrants from Jullundur and Hoshiarpur.Religious celebrations include all Gurpurbs.Marriage,Akhand Path and Sahaj Path. Sikh sangat is informed about various programs by Radio Fiji announcements. There are 5 Gurudwaras in different parts of fiji having one Kindergarten,three Primary schools and one khalsa […]




